Today is Jenkins’ Ear Day, also known as Jenkins’s Ear Day. It commemorates an event that took place on April 9, 1731, and remains one of the strangest rationalizations for war in human history.
 It’s difficult to find any time in the early 18th century when England and Spain weren’t at odds or war. At various points, diplomats were given the miserable task of trying to impose order. The Treaty of Utrecht of 1713 was one such attempt, signed as the War of Spanish Succession begun in 1700 wound down.
It’s difficult to find any time in the early 18th century when England and Spain weren’t at odds or war. At various points, diplomats were given the miserable task of trying to impose order. The Treaty of Utrecht of 1713 was one such attempt, signed as the War of Spanish Succession begun in 1700 wound down.
The agreement awarded England an exclusive 30-year contract to supply an unlimited number of slaves to the Spanish colonies. Although it allowed only 500 tons of goods per year, many traders, now able to weigh anchor for “legitimate” business purposes, used the opportunity to smuggle goods into and out of the Spanish colonies.
Skirmishes over trade and ongoing disputes about the contested land between the British colony of Georgia and Spanish-ruled Florida culminated in one of many Anglo-Spanish wars. Most historians agree it ran from 1727 to 1729; some say it began in 1726. With the level of hostility between the two nations, it was hard to tell when the war started.
In 1729, the Treaty of Seville was signed. One of its provisos gave the Spanish the right to board and search English vessels and to seize any contraband they found. It’s not surprising that mutual distrust and enmity resulted in the detainment and delay of many ships, regardless of suspicious activity. Captains began to report harrowing tales of abuse and theft of legal cargo.
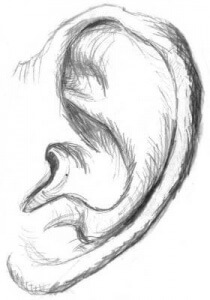
One such incident occurred on April 9, 1731, when the crew of a Spanish sloop from Havana, Cuba, boarded the British ship Rebecca and claimed to have found contraband. Not much is known about Captain Robert Jenkins. In some accounts, he is described as a master mariner; in others, he is called a notorious smuggler.
Jenkins may or may not have been lashed to his ship’s mast and tortured by Spanish captain Juan de Leon Fandino. Someone drew his cutlass and sliced off Jenkins’ left ear. According to Jenkins’ account, the blade was not entirely successful in removing the ear. Another Spanish sailor then grabbed it, tore it off and handed it to Jenkins, who was told to present it to his king with the message that Fandino would do the same to him.
We can’t be sure of the details as we don’t know if anyone on the Rebecca spoke Spanish or Fandino’s crew, English. We assume it would have been hard for Jenkins to hear, what with only having the one ear and that most likely being filled with the sounds of his own screaming.
In any case, his traumatic auriculectomy didn’t garner much concern in Parliament, possibly because it was in no hurry to start a fresh war. Perhaps it wasn’t considered too upsetting because the cropping of ears (and noses) was a common punishment dating back to the Babylonian Code of Hammurabi in 1754 BC.
One case worth mentioning took place in 1538 when Englishman Thomas Barrie was pilloried in the Newbury town square. To intensify his humiliation, his ears were nailed to the pillory on either side of the head hole. At the end of the day, he was released by having his ears cut off. He later died of shock.
What was Barrie’s crime? He spread rumors that Henry VIII had died. This displeased the king, who was very much alive and not amused. Barrie was the proto-Twitter troll. Imagine if this punishment were still in use today. There would be a lot of people cupping their hands to their heads, saying, “What? What?”
Back to our story. In 1738, politicians sought to gain support for a new war. Victory was expected to provide new business opportunities in Spanish America in part by forcing Spain to honor (and renew) the slave trade treaty which would expire in a few years. They needed to drum up outrage to generate nationalistic fervor.
Jenkins was called to testify before the House of Commons. Apparently, he was still attached to his ear, although it was no longer attached to his body. Afterward, some stories claimed he took it from his pocket where it was wrapped in cotton wool. Others insisted he had pickled and stored it in a jar, which he held aloft so that every member of the august assemblage might be afforded an unimpeded view.
A flaw in this version of events is that parliamentary records, normally exhaustive, show only that he was called to appear on two separate occasions. Surely a man brandishing an ear would have been noticed. Even without the visual aid, his visit would almost certainly have been documented, especially when it was to be used for political purposes.
It’s more likely that he was at sea. He was a ship’s captain, after all. If he returned after the war began in 1739, he wouldn’t have been amazed, as some histories suggest, to find the conflict was named after his ear. It didn’t become known as the War of Jenkins’s Ear until Thomas Carlyle coined the term in 1858, 110 years after it concluded.
Have a happy Jenkins’ Ear Day!

![]()

 The Kingsmen recorded the version most of us know in 1963. Singer Jack Ely’s unintelligible shouting—crappy microphones and Ely’s braces certainly didn’t help—led many to suspect the lyrics had been altered and must be “dirty.” Imaginations ran wild; teenagers invented ever more titillating interpretations.
The Kingsmen recorded the version most of us know in 1963. Singer Jack Ely’s unintelligible shouting—crappy microphones and Ely’s braces certainly didn’t help—led many to suspect the lyrics had been altered and must be “dirty.” Imaginations ran wild; teenagers invented ever more titillating interpretations.
 It’s difficult to find any time in the early 18th century when England and Spain weren’t at odds or war. At various points, diplomats were given the miserable task of trying to impose order. The Treaty of Utrecht of 1713 was one such attempt, signed as the War of Spanish Succession begun in 1700 wound down.
It’s difficult to find any time in the early 18th century when England and Spain weren’t at odds or war. At various points, diplomats were given the miserable task of trying to impose order. The Treaty of Utrecht of 1713 was one such attempt, signed as the War of Spanish Succession begun in 1700 wound down.